How Would You Describe the Shape of the Titration Curve
What species are the most important in determining the different regions. S shaped curve slow ph change in beginning and then drastic change in pH and then slow change in pH again.

21 4 Acid Base Titrations Flashcards Quizlet
A titration curve is a graph of pH vs.

. Volume Strong acid-strong base of titrant. There are four phases of a titration. At the beginning of this titration you have an excess of hydrochloric acid.
The curve consists of a plot displaying pH. In a weak acid-strong base titration the pH is greater than 7 at the equivalence point. The shape of a titration curve a plot of pH versus the amount of acid or base added provides important information about what is occurring in solution during a titration.
Name four factors bonds or other forces that contribute to stabilizing the native structure of a protein and describe one condition or reagent that interferes with each type of stabilizing force. How would you describe the shape of the titration curve. The shape of each titration curve is typical for the type of acid-base titration.
Label each titration curve below with the reaction that is occurring and the species present at each stage of the titration. At the beginning of the reaction only the strong acid is. A strong base is one that has relatively high dissociation in water A.
In this case the question indicates that the pH at equivalence was 89 which would correspond to a volume between 200 and 240 on the x-axis of the graph. What are the implications of the shape of the titration curve. Titrating 01 mol dm-3 base with 02 mol dm-3 acid.
A titration curve is a graphical representation of the pH of a solution during a titration. Why do you think the titration curve has the shape it has. The pH does not change in a regular manner as the acid is added.
The titration curve has a dramatic increase at the equivalence point because that is where the moles of base and acid are equal and the H ions have been used Volume titrant mL. The titration curve is an S shaped curve with a large jump at the equivalence point. H 3 O aq OH aq 2 H 2 O ℓ Figure 1 below shows a strong acid being titrated with a strong base.
There is also a very steep portion of each curve except for. Titration Curves A titration curve is drawn by plotting data attained during a titration titrant volume on the x-axis and pH on the y-axis. It is only after the equivalence point that things become different.
1 titration curves are the graphs drawn on the basis of the results obtained after doing the titration of your analyte with another reagent. If you understand that logarithm results in a compressed scale ie. At the equivalence point.
The titration curve serves to profile the unknown solution. Diagram of equivalence point. Up to 24 cash back Titration of a Strong Base with a Strong Acid Titration of a Weak Base with a Strong Acid When the sample solution is a base the shape of the graph is inverted If you compare these two graphs you should notice similarities as the previous example in the following.
1 on a question. The graph at right shows a typical titration curve for the titration of a strong acid by a strong base. Titrating 02 mol dm-3 base with 01 mol dm-3 acid.
For the rest of us plebeians there are a couple of things to bear in mind while you read this post. A strong base is one that has relatively high dissociation in water How would you describe the shape of the titration curve. After the equivalence point.
A titration curve is a graph of pH vs. The graph at right shows a typical titration curve for the titration of a strong acid by a strong base. Strong AcidStrong Base Titration Curves.
Up to 10 cash back Explanation. A strong base is one that has relatively high dissociation in water 공 Equivalence point A. Titration Curve with Equivalence Point.
Before the equivalence point. Before equivalence at equivalence and after equivalence. Try the given examples or type in your own problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.
It is drawn between the signal on the y-axis and volume of the reagent added from the burette View the full answer. Point in titration at which the amount of titrant added is just enough to completely neutralize the analyte solution. Strong acidstrong base titrations both use the same chemical equation to describe what is happening during the titration.
Understanding the shape of a titration curve. O the length of the steep portion o ph at the equivalence point. A quicker change from a high pH of around 83 to around 3 pH using less titrant.
Each curve has horizontal sections where a lot of bases can be added without changing the pH much. Acid-base titrations are monitored by the change. This leads to our approximate answer of 218mL.
In a strong acid-strong base titration the equivalence point is reached when the moles of acid and base are equal and the pH is 7. There are three major regions on a titration curve. Lg10 1 lg1002 etc you should be able to deduce the shape of the titration curve pretty quickly if you know the definition of pH.
Below is an Acid-Base Titration curve used to quantify the oxalic acid analyte using NaOH as a titrant. How do you describe the titration curves. Titration curves depend often strongly on the titration speed that is the time interval between the addition of each aliquot of acid and base and also the volume of each aliquot.
The shape of the curve will be the same as when you had an excess of acid at the start of a titration running sodium hydroxide solution into the acid. How does the shape of a titration curve confirm the fact that the pH region of greatest buffering power for an amino acid solution is around its pKs. Titration Curves Making sure you fully understand titration curves Try the free Mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various math topics.
Describe and explain how the shapes of your ph titration curves would be different for the following. The graph at right shows a typical titration curve for the titration of a strong acid by a strong base. In the shape of the curve lies much chemistry and an interesting summary of what we have learned so far about acids and bases.
The shapes of titration curves for weak acids and bases depend dramatically on. The titration curve is a graphical representation of a titration in which the volume of titrant is plotted on X-axis as the independent variable and the pH of the solution is plotted on the Y-axis as the dependent variable. For any titration curve the equivalence point corresponds to the steepest part of the curve.
Before the titration begins. Interface Science and Technology 2006. At the equivalence point in an acid-base titration moles of base moles of acid and the solution only contains salt and water.
The equivalence point of a system occurs during a vertical increase in its pH values while the endpoint of a visual indicator tends to occur during the last slight increase in pH value.

Virtual Lab Titration Mr Palermo S Flipped Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Virtual
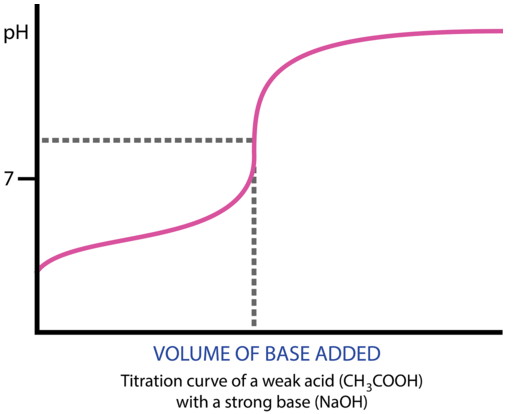
21 19 Titration Curves Chemistry Libretexts

Strong Acid Strong Base Titrations

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy

21 4 Acid Base Titrations Flashcards Quizlet
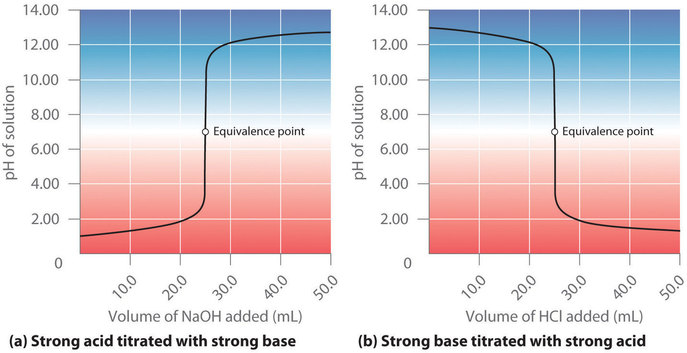
7 3 Acid Base Titrations Chemistry Libretexts
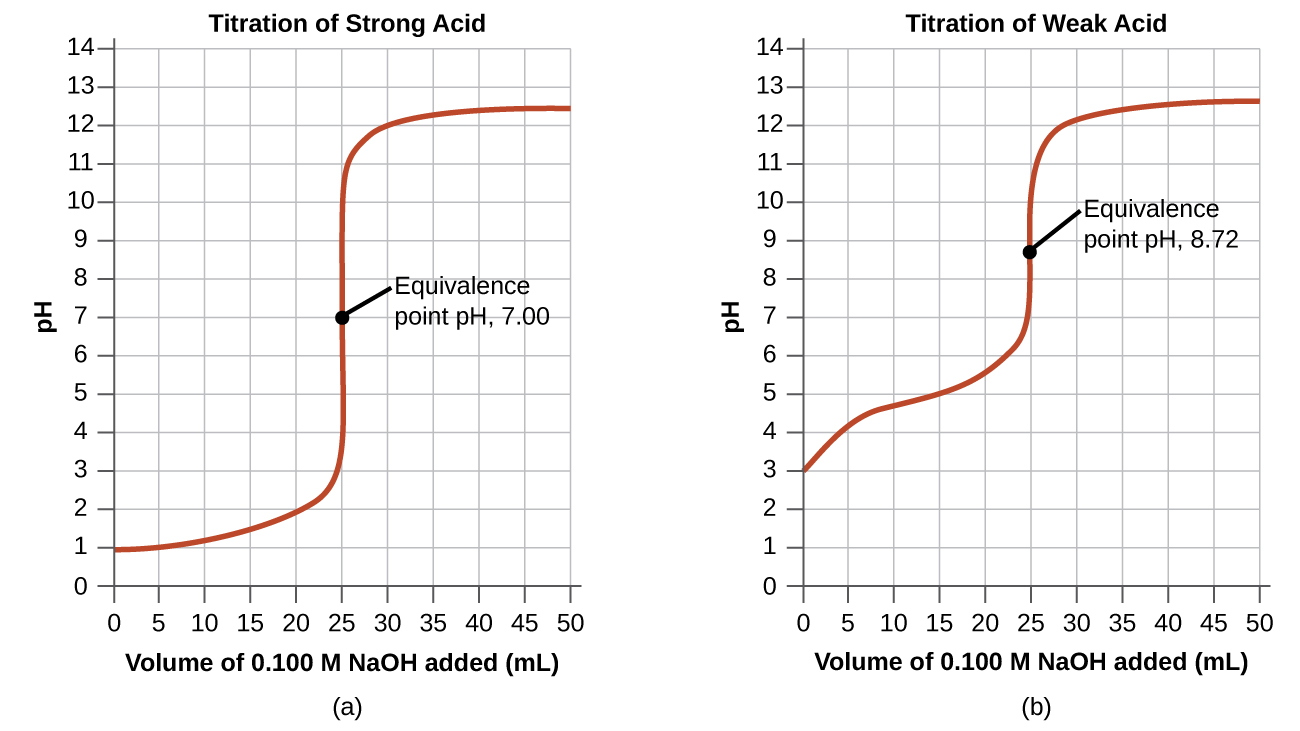
14 7 Acid Base Titrations Chemistry
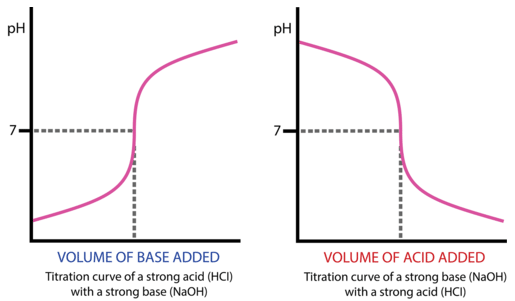
21 19 Titration Curves Chemistry Libretexts

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy

Colligative Properties Lower Vapor Pressure Chemistry Projects Chemistry Visual Learners

Titration High School Chemistry Labs Chemistry Lessons High School Chemistry

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy

Titration Curves Equivalence Point Article Khan Academy

Dcs For Hybrid Applications Plantstruxure Pes Plantstruxure Pillar Optimization Application Solutions




Comments
Post a Comment